We’re witnessing a particularly unexpected set of circumstances.
One: The vaunted Russian army is proving to be a shadow of its former self.
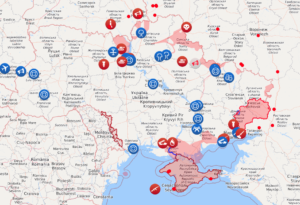
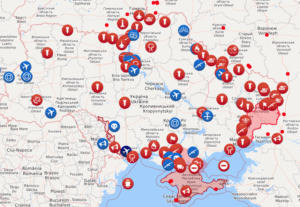
While the Russian pounding of Ukrainian cities increases, Kyiv remains in Ukrainian control, and Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelensky is still, at minimum, safe enough to record videos of himself walking to a hospital to visit wounded Ukrainian soldiers. In just three weeks, the Russian military has likely suffered more killed, wounded, and captured than the U.S. and U.K. did combined over the course of 20 years in Afghanistan. One site attempting to track the damage calculates that the Ukrainians have destroyed, damaged, or captured more than 1,200 Russian military vehicles and shot down or otherwise damaged 15 helicopters, 13 fixed-wing aircraft, six drones, two fuel trains, and more than 400 support vehicles.
If the Russian army was marching across Ukraine as planned, the Russians would not be attempting to recruit Syrian mercenaries.
This doesn’t mean that 200,000 Russian troops, with all their support vehicles, tanks, artillery, guided-missile systems, jets, helicopters, etc., cannot kill many Ukrainians and inflict extraordinary damage on the cities and homes and critical infrastructure of Ukraine. But it does mean that the Russian army is hampered by severe logistics problems, poor intelligence and tactics, persistent communications problems, awful morale, faulty equipment, and long-expired rations. Some significant portion of the great fortune that Russia spent to upgrade its military over the past two decades was skimmed off the top and diverted into someone’s pockets.
Polina Beliakova, a senior research fellow at the Center for Strategic Studies at Tufts University, contends that Putin’s wealthy allies were stealing from the military and shortchanging the troops right under Putin’s nose:
Most companies responsible for providing food to the Russian military are connected to Yevgeny Prigozhin — the patron of PMC Wagner, the mercenary organization, and sponsor of the Internet Research Agency, which has been accused of meddling in the United States elections. Several years ago, Prigozhin’s companies were accused by Russian opposition leader Alexei Navalny of forming a cartel and gaming the state’s bidding system for defense orders, receiving contracts for several hundred million dollars. The quality of food and housing in the Russian military is reportedly worse than in its prisons, with unreasonably small meals and some carrying harmful Escherichia coli bacteria.
Putin is now learning that hard lesson of former U.S. secretary of defense Donald Rumsfeld, “You go to war with the army you have, not the army you might want or wish to have at a later time.”
The army Russia has is nowhere near as effective as Putin thought it was. And the Eastern Europeans have noticed:
“Today what I have seen is that even this huge army or military is not so huge,” said Lt. Gen. Martin Herem, Estonia’s chief of defense, during a news conference at an air base in northern Estonia with Gen. Mark A. Milley, the chairman of the U.S. Joint Chiefs of Staff. General Herem’s colleague and the air force chief, Brig. Gen. Rauno Sirk, in an interview with a local newspaper, was even more blunt in his assessment of the Russian air force. “If you look at what’s on the other side, you’ll see that there isn’t really an opponent anymore,” he said.
Two: The Russian economy continues to freefall.
The Russian government announced that they intend to pay back their debts in now-almost-worthless rubles. The Moscow Stock Exchange will stay closed until at least March 18. The Financial Times’ European banking correspondent, Owen Walker, says the Russian Ministry of Finance can keep the big Russian banks going for a while, but in the end, the Russian companies will have no money coming in from countries enacting sanctions.
Maybe India can help with this problem, but it will cost Russia; the Indian government is reportedly interested in buying Russian oil at a discount. Russia not only wants economic assistance from China, but has reportedly asked for military assistance as well, in the form of drones.
Three: Despite all of this, Putin is not only undeterred, he wants to double down.
Back in 2014, when Russian military forces moved into Crimea and annexed it, then-secretary of state John Kerry and other Obama administration officials kept talking up the option of a “diplomatic off-ramp” that would end Russia’s military occupation. Those proposals never went anywhere; Kerry seemed to be in denial of the fact that Putin was on precisely the highway he wanted to be on, headed toward exactly the destination he wanted. Putin wasn’t looking for an “off-ramp.”
Today, you hear the same refrain — that if the West just tried hard enough, it could find some “diplomatic off-ramp” that would be acceptable to Putin:
Axios: “President Biden now faces a great unanswered question — how to give Vladimir Putin an off-ramp to avoid even greater calamity.” The Irish Times: “While the prospect of a ceasefire in the short-term may seem remote, there will come a point where Putin needs an off-ramp. The West can keep applying pressure on Putin while showing him that a negotiated peace is there for the taking.” NPR: “Diplomats are trying to find an off ramp to Putin’s war in Ukraine.”
How can Putin make it any clearer? He doesn’t want an “off ramp!” He doesn’t want to end his war, he wants to win his war. He doesn’t care how gargantuan a price he or his country must pay in blood and treasure to achieve victory. To a certain degree, Putin is dealing with the sunken-cost fallacy. He has already committed so much, nationally and personally, into this war that he cannot accept a relatively modest prize of Donetsk and Luhansk and a guarantee that Ukraine would never join NATO. Russia’s big sacrifices in this war means Putin must bring home a big prize to justify the bloody endeavor.
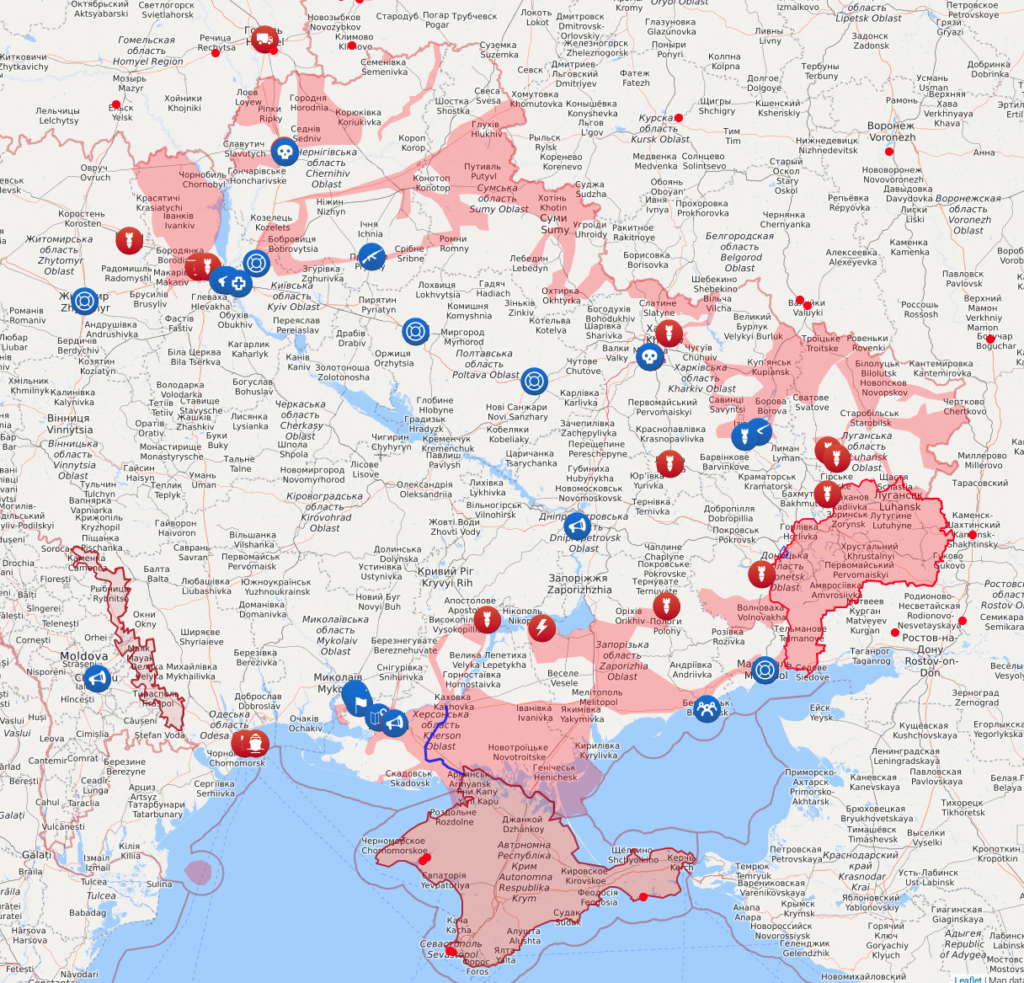
 Ukraine Weapons Tracker (@UAWeapons)
Ukraine Weapons Tracker (@UAWeapons)